It is use the most frequently used circuit in electronic DC power supplies. It converts the full cycle of AC in to DC.
Four diodes and a transformer are used in it. Since, the whole secondary winding of transformer is used in this circuit, so it produces double volts than full wave centre tapped rectifier.
Working Principle
The input of transformer is provided an AC supply.
When the input gets a positive half cycle, the upper end ‘A’ of secondary winding becomes positive and lower end ‘B’ becomes negative. In this condition the diodes D1 and D3 become forward biased and switch to ON condition. And the diodes D2 and D4 are reversed biased and switched to OFF condition. The conventional current starts from point ‘A’ and travels through D1 load and D3 to complete its circuit.( As shown in figure 1).
When the input gets negative half cycle then point ‘A’ becomes negative and point ‘B’ becomes positive. In this condition, the diodes D2 & D4 are forward biased and switched to ON condition. While the diodes D1 & D3 become reverse biased and switched to OFF condition. The current starts from point ‘B’ travels through D2 , load and D4 to complete its circuit. (Shown in figure 2).






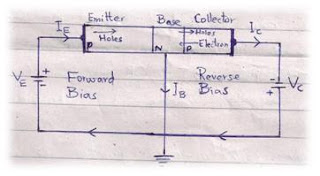












.jpg)



